advanced-js-reading-notes
AWS: S3 and Lambda
AWS S3
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service offering industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. Customers of all sizes and industries can store and protect any amount of data for virtually any use case, such as data lakes, cloud-native applications, and mobile apps. With cost-effective storage classes and easy-to-use management features, you can optimize costs, organize data, and configure fine-tuned access controls to meet specific business, organizational, and compliance requirements.
AWS Lambda Basics
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). Users of AWS Lambda create functions, self-contained applications written in one of the supported languages and runtimes, and upload them to AWS Lambda, which executes those functions in an efficient and flexible manner.
The Lambda functions can perform any kind of computing task, from serving web pages and processing streams of data to calling APIs and integrating with other AWS services.
Due to Lambda’s architecture, it can deliver great benefits over traditional cloud computing setups for applications where: individual tasks run for a short time; each task is generally self-contained; there is a large difference between the lowest and highest levels in the workload of the application.
It is easy to integrate AWS Lambda with datasources like Amazon DynamoDB and trigger a Lambda function for specific kinds of data events.
Both existing and new accounts get 1 million AWS Lambda requests plus 400,000 GB-seconds per month — Lambda’s measure of function runtime and the memory allocated to a function.
Total compute: 30 days x 600 GB-seconds (10 minutes) = 18,000 GB-seconds Total requests: 30 days x 1 request per day = 30 requests This usage is within the AWS free tier, so you’ll be charged $0 for AWS Lambda.
With the Serverless Framework, you can create Lambda functions using the tools you’re familiar with on your local machine and deploy to AWS in seconds.
AWS Lambda Functions
AWS Lambda is a serverless, event-driven compute service that lets you run code for virtually any type of application or backend service without provisioning or managing servers. You can trigger Lambda from over 200 AWS services and software as a service (SaaS) applications, and only pay for what you use.
Read more from here for more details
CDN
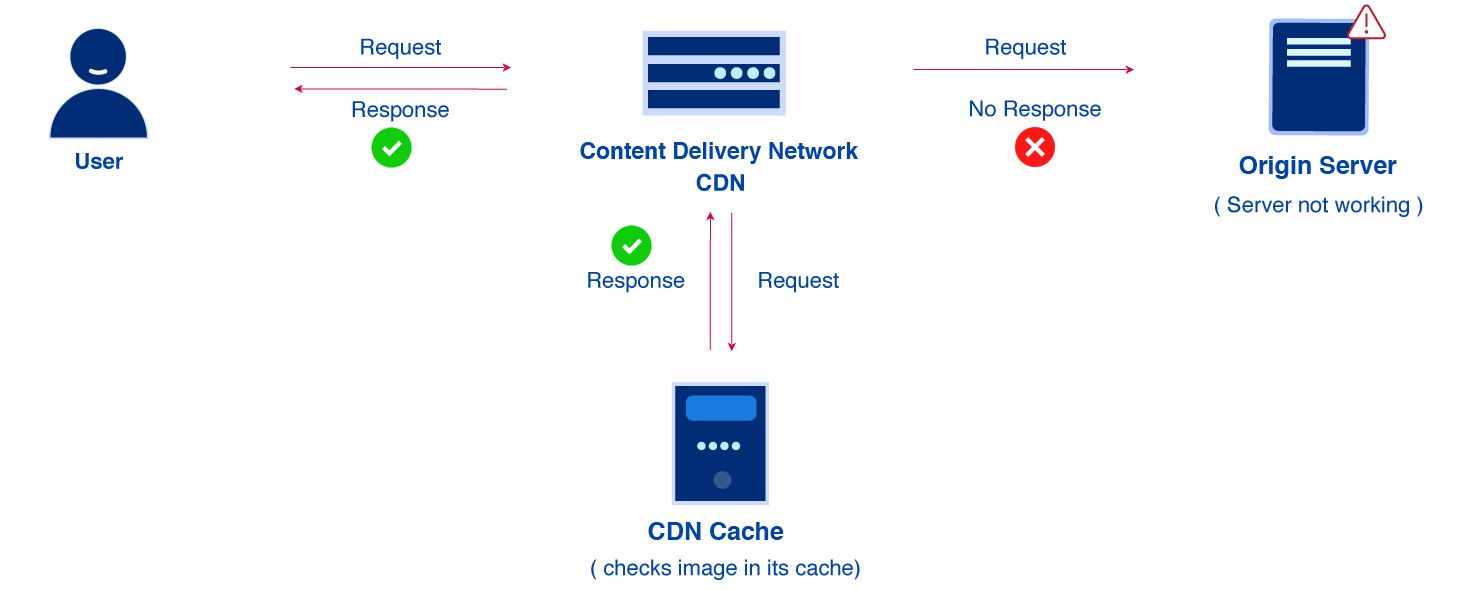
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a geographically distributed group of servers that work together to provide fast delivery of Internet content. A CDN allows for the fast transfer of data needed for loading Internet content including HTML pages, javascript files, stylesheets, images, and videos.
CDNs work through servers nearest to the website visitor respond to the request.
The content delivery network copies the pages of a website to a network of servers that are spread out at geographically different locations, caching the contents of the page.
When a user requests a webpage that is part of a content delivery network, the CDN will redirect the request from the originating site’s server to a server in the CDN that is closest to the user and deliver the cached content.
Employing a CDN doesn’t only speed up the delivery of Internet content, it helps protect your website against certain forms of cyber attacks, such as Denial of Service attacks.
Source: CloudFlare, Webopedia Additional Reading: Pantheon’s Advanced Global CDN to Further Enterprise Open Source Adoption Related Terms: Denial of Service (DoS), Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)